How to protect yourself and colleagues from persuasive social engineering “specialists”
How could it be that Olena downloaded the virus, believing that by following the link she would receive a brand new iPhone as a gift? Did Oleksiy do better than Elena by inserting a pretty flash drive with an interesting logo that he had just found in a cafe into his work computer? Both became victims of social engineering.
What is social engineering
In general, social engineering is a science that studies human behavior and factors (circumstances, environment, personal value system) that can influence it. But this term is widely used among information security specialists in the sense of psychological manipulation, which is carried out by fraudsters in order to obtain confidential information from network users (or company employees).
Such fraudsters are often called “specialists” in social engineering. It is not for nothing that we put the word “specialists” in quotation marks, because the context of the word here is not at all positive. We must admit that their manipulations work well – in 65% of cases, fraudsters achieve their goals where the system is reliably protected by hardware methods.
The human factor becomes a weak link in it, because a person has feelings and is prone to emotional states, unlike technology. So, under certain circumstances, a person can disclose information even to strangers, trusting them for some reason.

Methods used by fraudsters to obtain information
To obtain information, fraudsters primarily use such human weaknesses as fear, curiosity, inattention, inexperience. If the attackers have an advanced level and more far-reaching goals, they try to make friends with the victim, gain trust by communicating with them for some time.
The methods by which criminals obtain the information they need are called:
- Pretexting (pretext).
- Phishing (email phishing or phone phishing).
- Road apple.
- Shoulder surfing.
- Quid pro quo (service for service).
Pretexting

The essence of this method is that the victim performs actions that the attackers push him to do according to a previously developed script. This can be the disclosure of some data, or the download of malicious software. To develop a suitable scenario, fraudsters first track down the victim, collect data about him and the company he works for: full name, date of birth, position, department name, name of projects he works with, name of employees, etc. The attacker tries to find out about the missing elements through the social network (for example, by hacking the accounts of friends in social networks).
Having obtained the necessary information, the fraudster can impersonate another person, already communicating with the head of the unit. Having collected data about the middle manager, he already turns to his supervisor. And so he acts until he gains access to the bank accounts of the company or hacks the account of the super administrator on the site.
Phishing
Phishing can vary according to the method of communication: written (97%), spoken (2%) or a combination of them (1%).
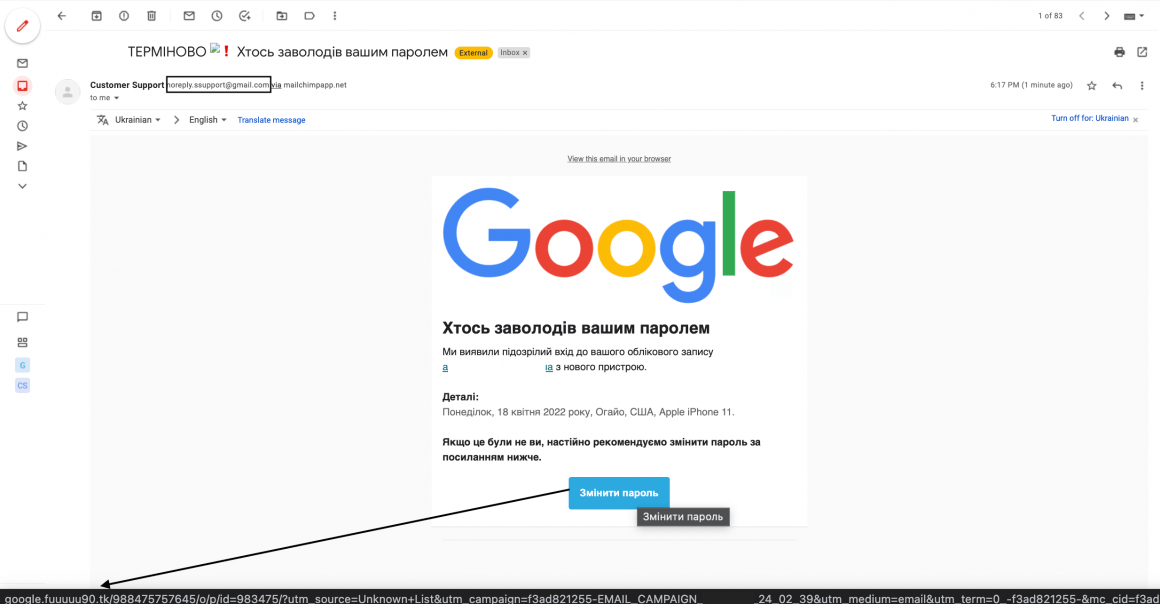
Phishing in correspondence
Email is the most common type of phishing. It is based on sending the victim an SMS notification or a letter to the mail with malicious software or a fake site with a data entry form. To identify a fake site, you need to pay attention to its address.
In order for the user to open the message and follow the link, the attacker fakes it as an appeal from banks, government agencies, security services, police, volunteer organizations, etc.
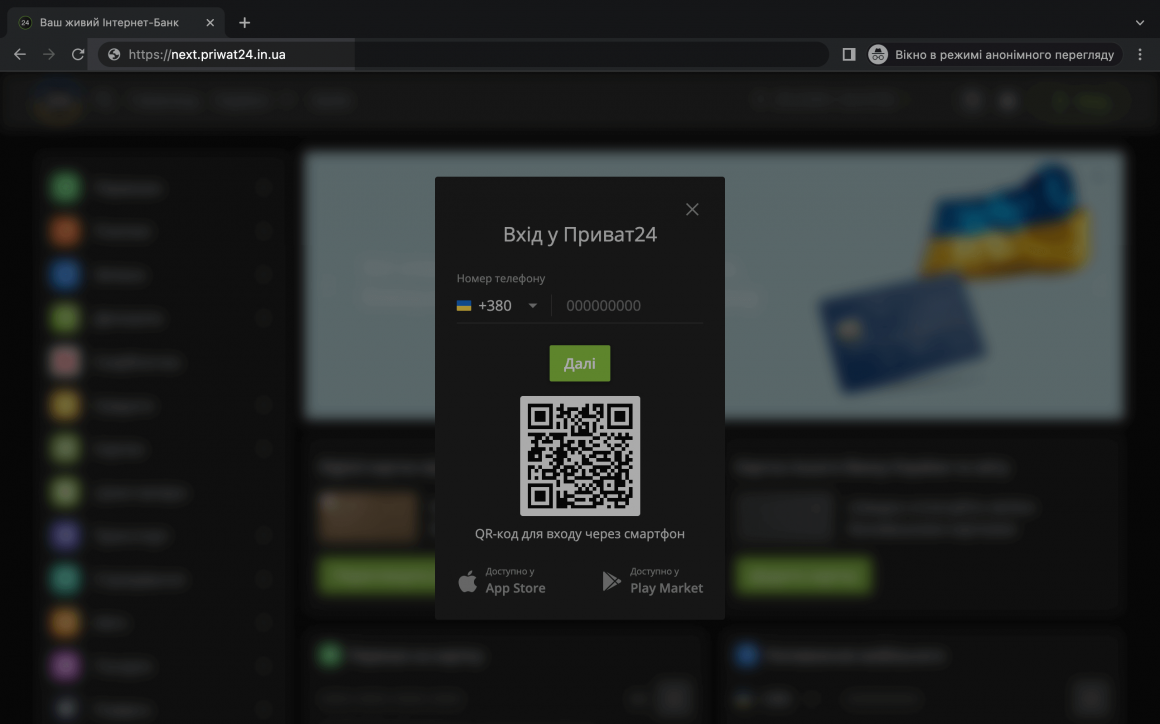
An example of a fake page, the address of which differs by one letter and has an additional level of the “in” domain.
Key phrases that Internet users respond to more often:
- “Your financial accounts are blocked, enter your card details to unlock.”
- “We are collecting money for a drone (helmets, clothes, food), send a certain amount.”
- “Congratulations, as a regular customer of our supermarket, you have won a phone/computer/car/apartment under our promotion.”
- “Your computer system is not protected, please update your antivirus.”
- “Your property documents have been removed from the registry, please upload them again.”
- “An error with the calculation of wages, for confirmation, send the data of the passport and bank card.”
Phone phishing
Phone phishing is even more dangerous than correspondence, because in this case it is easier for the fraudster to create conditions for urgent action, when the victim does not have time to think. And when a person is in a hurry, he often makes mistakes.
The topics that phone fraudsters cling to are similar to those we talked about in the previous paragraph, but other manipulations related to the need for an urgent solution may be added to them:
- relatives got into an accident;
- the man was detained by the police;
- your brother is in trouble due to heavy debts etc.
In addition, fraudsters use the “official call” method from banks, services or the police. They are presented by other persons and completely copy the style of official messages, so people usually believe them.
There are also cases when the victim is first sent a letter, and then additionally calls so that she is sure to open it and receive a “Trojan horse” (malicious software under the pretext of downloading a supposedly safe file).
Road apple

This method is similar to a “Trojan horse”. Only it consists in the fact that a physical medium (flash drive) is thrown to the victim, which activates a ransomware virus or a spy virus. The media has a good look, official logos to attract attention. It seems that someone loses it in public places: in a café, a co-working space, in a parking lot, in a sports club, a room for workers to change clothes/smoking, etc. And when a person inserts the find into a personal / work device, he gets troubles, such as: blocking of programs, changes in databases, theft of passwords.
Shoulder surfing

This method is not very simple and involves observing the victim in public places. And although everyone may think that they will be able to notice the person who is watching them in time, this is not always the case. Because attackers can work in a team, and one of them can distract the user’s attention, and the second can stand behind him. In this way, attackers can not only see the PIN code from the card (which a person enters at an ATM or at the checkout in a supermarket), but also spy on the two-factor authentication message code on the phone/laptop screen.
In the second case, he works according to the following method: he receives the phone number of the victim, for example, in social networks. Then, while she’s standing somewhere in line, the scammer dials a password reset feature with a text message on her phone. Unsuspecting, a person takes out a phone, on the screen of which a message with a code appears. In this way, the attacker opens an account in social networks and gets access to all linked services.
Quid pro quo

An example of dialogue in a large company, where specialists from different departments hardly cross each other.
| – Hello! I’m Andrii from the technical department. How can I contact you? – Hello! My name is Maksym. — Nice to meet you. Have you ever had network problems? – No, it’s okay. — OK, and what is your computer number? — ХХХХХ123. And why do you ask? — The thing is that there is an emergency situation in the neighboring block, so they are warning about a long shutdown. Will it not be a problem for you to work for 2-3 days without the Internet? — What about you! I can last a couple of hours at most. — OK, then call my phone if you have any problems. Можемо запропонувати альтернативне підключення. After that, the attacker calls the real technical department and says: |
After being without the Internet for an hour, Maksym usually starts calling “Andrei” to “help” him solve the situation. In turn, “Andriy” sends Maksym alleged connection software, but in fact a “Trojan horse”. After that, he calls the technical department again and asks to connect the computer, because “testing is completed”.
Why did everyone believe “Andrei” in this situation? Because a technical specialist who can solve network issues is undeniably trustworthy. And for the technical department, the name of the employee and the name of the computer turned out to be enough factors not to check who is actually calling. Although the technicians could have asked more questions to the attacker (what testing, for what, do you need to send one of ours to you). And Maxim could ask his colleagues if they have similar problems with the network.
How to find out that social engineering methods are being applied to you
Recognizing malicious attacks can be difficult. Especially when you are multitasking and suddenly receive a message allegedly from a company or government service. But some nuances should alert you:
- The need for urgent confirmation of some personal data — usually enough time is allocated for any confirmation of the request so that the person can have time to collect information and prepare documents. Fraudsters deliberately put pressure on the victim to prevent them from thinking about their decision.
- Request passwords, PIN codes, personal information, personal accounts, documents — no service has the authority to make such requests. Even if the message says that certain documents are required to receive a salary, put the call on hold, call the accounting department, contact the administration and find out if they really sent you a letter. Or even ask colleagues if they have received similar requests.
- Notification of a big win or receiving an inheritance from distant relatives from abroad — yes, that may be true, but it usually doesn’t require urgent tax payments on a voice-over-the-phone bill to get it. If it is about winning, then you will be asked to confirm the participant of the promotion – it can be numbers from a lottery ticket or a secret word under the lid, etc. If we are talking about inheritance, then most likely you will first receive an invitation to personally visit the relevant authority, taking with you the documents that will be listed in the sent list.
- The interlocutor speaks the name, position, or company very quickly. If fraudsters have little information, they rely heavily on the inattention of the interlocutor, so they very quickly get to the point and deliberately speak some data unintelligibly (they can even create artificial interference on the network). It is enough to calmly ask the name, position, and name of the company so that the attacker will apologize and, under the pretext of calling back later, hang up.
- The need to send funds to an account number that must be entered manually, or through unfamiliar, dubious services on insecure sites. Usually, paying through quality stores or sending funds for assistance is done through official payment channels with one button (for example, through the Google Pay service), and not through online banking. And for this you do not need to manually dial the account number.
How to protect yourself from “specialists” in social engineering
To protect yourself from the influence of fraudsters, we advise you to follow the recommendations of cybersecurity experts:
- Try to be aware of social engineering techniques.
- Include a critical attitude to any messages.
- Put your calls on pause, so you can mull over the strange message.
- Do not hesitate to ask the interlocutor the name, position, name of the department, company, etc.
- Check the truth of the facts through additional channels of communication so that you cannot be intimidated or misled by bad news from relatives.
- Consult relatives, acquaintances before giving an answer regarding winnings or inheritance.
- Check the sender’s data: whether there are no errors in the browser/mail address, whether the phone number is different from the official one on the website.
- If you are asked for money for help, transfer funds only through official services.
- Do not pick up flash drives or insert them into the computer without prior verification by specialists.
- Replace credit card payments with phone or smartwatch payment confirmation. Forget about entering PIN codes in public places.
- Check files for viruses before downloading them.
- Protect your accounts with two-factor authentication. More about it in our article: “Two-factor authentication”.
Separately, we highlight measures to protect employees of companies from intruders:
- Conduct regular cybersecurity training, especially for newcomers.
- Limit the rights of new users as much as possible. For example, prohibit downloading programs or using flash drives.
- Install reliable antivirus programs on every corporate computer.
- Prohibit the use of credentials anywhere outside the company.
- Develop a code of conduct in cases of confidential information requests.
- Prohibit the publication of personal data and contact information in public profiles of social networks (if the employee does not hold a relevant position that involves personal communication with clients, journalists, opinion leaders and does not engage in public work, etc.);
- Enter the use of technical means to protect accounts, such as: biometric scanners, smart cards, security keys.
All these methods are very effective, and their use will significantly help to avoid the negative influence of “specialists” in social engineering. Of course, in order to provide more actionable recommendations, cybersecurity experts need to learn more about the specifics of your business, perform penetration tests, talk to your employees, and more.
If you need to build a reliable security system for your company, contact our specialists. As professionals with 30 years of experience, we will help find system vulnerabilities and eliminate them, offer reliable cloud solutions so that you do not have to buy additional equipment, and recommend the most appropriate technical means of protecting employee accounts for the specifics of your business. Our contacts.
Don’t put off the security of your business for later. Contact us today!
